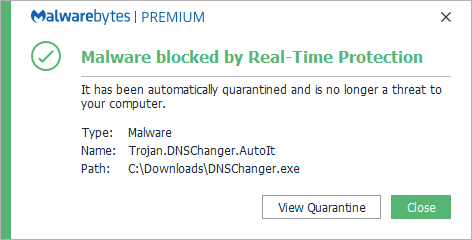
Trojan.DNSChanger
ThreatDown is now the name of the Malwarebytes line of business products. References to Malwarebytes below reflect the amazing technology used to first identify the threat.
Short bio
Trojan.DNSchanger is Malwarebytes’ generic detection name for Trojansthat change a systems’ DNS settings without the user’s knowledge or consent.
Type of infection
Once the systems are infected by Trojan.DNSChanger and their DNS settings modified, systems use foreign DNS servers set up by the threat actors. Infected systems that attempt to access specific sites are redirected to sites specified by these threat actors.Domain Name System (DNS) is known as an Internet standard for the assignment of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses to domain names. Simply put, DNS interprets human-friendly host names to PC-friendly IP addresses.It is common for users to automatically use DNS servers operated by their ISPs. Users who prefer more secure, faster, and reliable DNS servers usually go with a third-party serviceas ISP-administered DNS servers can be slow and unreliable.DNS changers/hijackers are sometimes bundled with other malware, such as rootkits, for example in the old TDSS family. Fake antivirus (FakeAV) programs have also been used to spread DNS changer Trojans, as seen in Rove Digital.
Business remediation
How to remove Trojan.DNSChanger with the Malwarebytes Nebula console
You can use the Malwarebytes Anti-Malware Nebula console to scan endpoints.
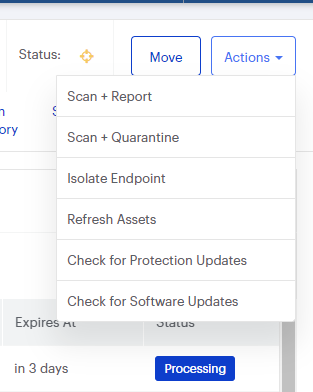
Nebula endpoint tasks menu
Choose the Scan + Quarantine option. Afterwards you can check the Detections pageto see which threats were found.
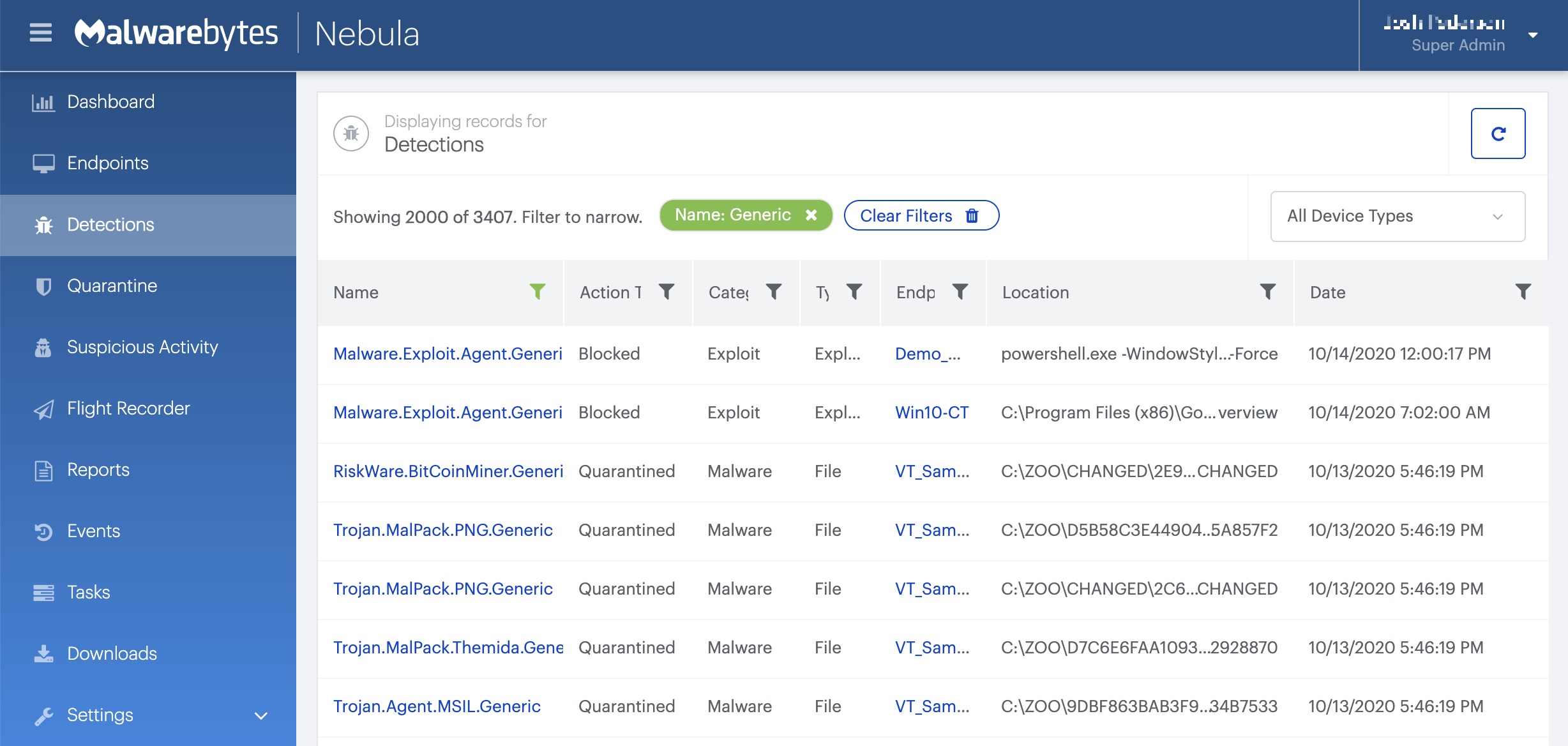
On the Quarantine pageyou can see which threats were quarantined and restore them if necessary.
A reboot is often required to flush the “poisoned” DNS cache.
Home remediation
Malwarebytes can detect and remove Trojan.DNSChanger without further user interaction.
- Please download Malwarebytesto your desktop.
- Double-click MBSetup.exeand follow the prompts to install the program.
- When your Malwarebytes for Windowsinstallation completes, the program opens to the Welcome to Malwarebytes screen.
- Click on the Get started button.
- Click Scan to start a Threat Scan.
- Click Quarantineto remove the found threats.
- Reboot the system if prompted to complete the removal process.
A reboot is often required to flush the “poisoned” DNS cache. Malwarebytes will prompt you to do this if needed.